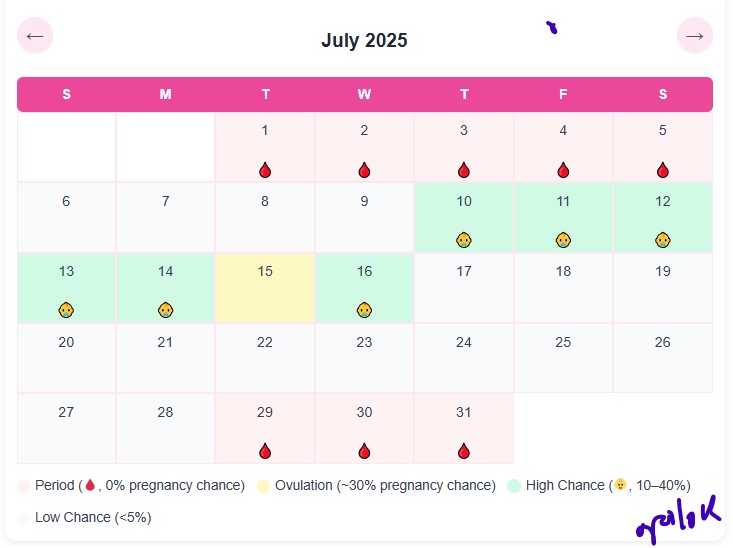
Advanced Period CalculatorEnter Period DetailsDetailed Cycle ReportS M T W T F S
Period (🩸, 0% pregnancy chance)
Ovulation (~30% pregnancy chance)
High Chance (👶, 10–40%)
Low Chance (<5%)
Cycle ProgressCycle TimelineEstimated Ovulation DateEstimated Period Dates |
Key phases of the menstrual cycle :
-
Menstruation: This phase begins the cycle. The uterus sheds its lining, resulting in menstrual bleeding that typically lasts 3 to 7 days. This occurs if pregnancy has not taken place, as hormone levels of estrogen and progesterone drop.
-
Follicular Phase: Starting on the first day of menstruation and lasting until ovulation (about 13–14 days), the brain’s pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), prompting ovarian follicles to develop. One follicle matures into an egg, and increasing estrogen causes the uterine lining to thicken in preparation for possible implantation.
-
Ovulation: Around the mid-point (day 14 in a classic 28-day cycle), a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of the mature egg from the ovary. This is when a woman is most fertile. The released egg travels down the fallopian tube, where it may encounter sperm and be fertilized.
-
Luteal Phase: After ovulation, the ruptured follicle forms the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to further thicken the uterine lining. If the egg is fertilized and implants, hormone levels remain high, sustaining the pregnancy. If not, the corpus luteum degrades, progesterone and estrogen fall, and the cycle restarts with the next period
Key factors influencing cycle length and regularity:
-
Age: Cycle length often varies in adolescence and again during perimenopause. Adolescents may take several years to develop regular cycles, and cycles can become more irregular as menopause approaches.
-
Genetics and Family History: There is a genetic component to both the timing of menarche (first period) and the tendency for regular or irregular cycles.
-
Lifestyle (including stress and physical activity): Stress, changes in exercise routines, and not getting enough calories can disrupt hormone signals, impacting regularity.
-
Body Weight: Both significant weight gain and loss, as well as obesity or being underweight, can change hormonal balance and alter the cycle.
-
Diet and Nutrition: Poor diet or extreme dietary changes may affect menstrual hormones and cycle stability.
-
Sleep Patterns: Irregular sleep or frequent time zone changes (jet lag) can influence your body’s reproductive hormones and cycle pattern.
-
Use of Contraceptives/Medications: Starting, stopping, or switching birth control methods, as well as certain other medications, can result in missed or irregular periods.
-
Medical Conditions: Disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, diabetes, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and others can disrupt menstrual regularity.
-
Alcohol and Smoking: Both have been linked to subtle menstrual changes, especially with high consumption or long-term use.
-
Socioeconomic and Environmental Factors: Socioeconomic status, urban vs. rural residence, and even exposure to air pollution or climate variations may play a secondary role.
-
Early Life and Intrauterine Factors: Birth weight, maternal health during pregnancy, and early childhood development can have long-term effects on cycle regularity.
Signs of Ovulation ( Period Calculator)
Ovulation occurs about midway through the menstrual cycle and is the period when a mature egg is released, making it the most fertile time. Some signs and symptoms that can indicate ovulation include:
-
Change in cervical mucus: Mucus becomes clear, slippery, and stretchy—much like raw egg whites. This helps sperm move more easily toward the egg.
-
Mild cramping or pain in the lower abdomen: Known as mittelschmerz, this discomfort is usually felt on one side and results from the egg being released from the ovary.
-
Slight increase in basal body temperature: After ovulation, resting body temperature rises slightly (about 0.3–0.6°C or 0.5–1°F).
-
Breast tenderness: Some women notice that their breasts become more sensitive.
-
Light spotting or discharge: Rarely, a small amount of blood or brown discharge may occur.
-
Heightened senses: Some may experience sharper senses of smell, taste, or vision.
-
Libido changes: An increase in sex drive often happens around ovulation.
-
Cervical changes: The cervix becomes softer, higher, and more open if you check manually.
-
Bloating or mild abdominal fullness.
Not everyone has noticeable ovulation symptoms, and some may only experience some of these signs intermittently.
Signs of an Approaching Period Calculator
“Period” or menstruation is the monthly shedding of the uterine lining. Signs that your period is about to begin (often called premenstrual syndrome, or PMS) in the days or week before menstruation include:
-
Abdominal cramps: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen. Can start before and continue into your period.
-
Bloating: Sense of fullness or swelling in the abdomen.
-
Breast tenderness or swelling: Breasts may feel sore or larger.
-
Mood changes: Such as irritability, anxiety, sadness, or mood swings.
-
Food cravings: Desire for specific foods, often carbohydrates or sweets.
-
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or low on energy.
-
Headaches or back pain.
-
Breakouts (acne): Pimples, especially on the chin or jawline.
-
Sleep changes: Trouble falling or staying asleep, or sleeping more than usual.
-
Changes in discharge: Vaginal mucus may decrease or become absent right before your period.
-
Emotional symptoms: Such as increased sensitivity or crying spells.
Not everyone experiences every symptom each cycle, and some may have more pronounced PMS than others.
Summary Table – Period Calculator
| Ovulation Signs | Period (PMS) Signs |
|---|---|
| Clear, stretchy cervical mucus | Cramps or lower back pain |
| Mittelschmerz (one-sided pain) | Bloating |
| Slight rise in temperature | Breast tenderness/swelling |
| Breast tenderness | Mood swings/irritability |
| Light spotting | Headache/fatigue |
| Heightened senses | Acne breakouts |
| Increased libido | Appetite changes |
| Cervical changes | Sleep changes |
| Bloating, mild abdominal fullness | Decreased vaginal discharge |
You should consult a doctor for irregular periods if you experience any of the following:
-
You miss your period for 3 months or more (and are not pregnant).
-
Your periods occur less than 9 times in a year.
-
You have not started your period by age 16–17.
-
Heavy bleeding: Soaking through a pad or tampon every hour or passing blood clots larger than a quarter.
-
Your periods consistently last longer than 7–8 days.
-
Bleeding between periods, after sex, or after menopause.
-
Sudden change in menstrual pattern: Periods become extremely irregular, much shorter or longer than usual.
-
Severe pain or cramping that interferes with daily life, or pelvic pain beyond normal discomfort.
-
Symptoms of anemia such as unusual tiredness, weakness, dizziness, or fainting—this can result from excessive blood loss.
-
Other symptoms along with irregular periods, such as unexplained weight gain or loss, new facial hair growth or hair loss, fatigue, or difficulty getting pregnant
Menstrual Cycle Calculator Tips :
-
Track First Day of Bleeding: Always input the first day of your period as “Day 1”—this is when menstrual bleeding starts, not spotting.
-
Record Each Cycle Consistently: Input the start date of your period each time. The calculator will use this to estimate your average cycle length and predict ovulation and next period dates.
-
Note Flow and Symptoms: Some calculators let you enter flow intensity, cramps, headaches, or PMS symptoms. The more you log, the more accurate your analysis over time.
-
Monitor Irregularities: If you miss periods, experience them much earlier or later than predicted, or notice unusual symptoms, record those details. A calculator can reveal patterns (or lack thereof) and help you share specifics with your healthcare provider.
-
Use for Ovulation Tracking: Use the calculator’s ovulation estimator for fertility purposes, but remember it is approximate—especially with irregular cycles. Watch for ovulation signs like changes in cervical mucus or basal body temperature to increase accuracy.
-
Set Reminders: Many apps or calculators offer reminders before your period or ovulation window. Activate these notifications to stay prepared.
-
Contextualize Your Results: Don’t rely solely on predicted dates—cycle length can naturally vary due to stress, illness, travel, or life changes. Use calculator predictions as a guide, not an absolute.
-
Share Data with Your Doctor: If you’re seeing a healthcare professional for cycle issues, export or screenshot your cycle data to provide comprehensive information.
Best Practices
-
Track at least 3–6 months of cycles for the most useful average and predictions, especially if your periods are usually irregular.
-
Combine digital tracking with your own notes about lifestyle factors (e.g., weight change, stress, or medication), as these can explain changes in your cycles.
-
If symptoms worsen or cycles become highly irregular despite using the calculator, consult your healthcare provider.
Using the calculator regularly as part of your cycle awareness routine can empower you to spot patterns, predict periods, prepare for symptoms, and flag changes that may warrant medical advice. Always combine tracking technology with attention to your body’s unique signals and guidance from healthcare professionals.
🌸 Why Period Tracker ? Track Your Cycle ?
Your menstrual cycle is more than just a monthly reminder — it’s a vital sign of your overall health. A Period Calculator can help you stay in tune with your body, track fertility, and manage symptoms like mood swings or cramps. Whether you’re trying to conceive or just want to know when to pack an extra pad, a period tracker is your personal health ally.
Let’s take a closer look at a real example from this month to see how it works.
📅 Example Cycle Overview
-
Last Period Started: Thursday, May 1, 2025
-
Cycle Length: 28 days
-
Period Length: 7 days (May 1 to May 7)
This sets the rhythm of your body for the rest of the month.
🔍 Fertility & Ovulation Breakdown
| Phase | Dates | Notes | Chance of Pregnancy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Period | May 1 – May 7 | Bleeding phase (0% fertility) | ❌ Very Low |
| Low Chance | May 8 – May 9 | Just after period | 🔻 Under 5% |
| High Chance | May 10 – May 16 | Fertile window | 🔺 10–40% |
| Ovulation | May 15 (Thursday) | Peak fertility | 🌟 ~30% |
| Next Period | May 29 – June 4 (Expected) | Cycle restart | 📌 Plan ahead |
🗓️ Monthly Fertility Calendar
🔸 🩸 Period Days
🔸 ⚪ Low Fertility Days
🔸 🔺 High Fertility Days
🔸 🌟 Ovulation Day (Peak)
📊 Summary Report
-
Cycle Length: 28 Days
-
Bleeding Duration: 7 Days
-
Ovulation Day: Thursday, May 15,
-
Fertile Window: May 10 to May 16
-
Next Expected Period: May 29 – June 4,
-
Best Time to Conceive: May 13 to May 16
🧘♀️ Helpful Tips
-
Track symptoms daily (mood, cramps, flow).
-
Stay hydrated and eat iron-rich foods during your period.
-
Plan around ovulation if you’re trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy.
-
Use a digital tracker or calendar (like the one above) to stay consistent.
❤️ Final Thoughts
Knowing your menstrual cycle helps you connect with your body in empowering ways. It’s not just about avoiding surprises — it’s about understanding yourself better.
Explore our Free Period Calculator Tool on Gollok.com to predict your future cycles, track symptoms, and feel in control every month.
🌼 Your cycle, your strength.
Research suggests ovulation typically occurs 14 days before the next period, with the fertile window being 5 days before and the day of ovulation, showing varying pregnancy chances.
It seems likely that period days have 0% pregnancy chance, low chance days <5%, and higher chance days 10–40%, peaking at ~30–40% around ovulation.
The evidence leans toward standard calculations for cycle length (21–35 days) and period length (3–10 days), with probabilities adjusted accordingly.
Calculation Overview
The period calculator uses standard medical guidelines to estimate ovulation and fertile windows. For a typical 28-day cycle:
- Period Days (Days 1–7): Marked with a red blood icon (🩸), 0% pregnancy chance.
- Low Chance Days (Days 8 and 16–28): Neutral background, <5% chance.
- Higher Chance Days (Days 9–15): Marked with a baby icon (👶), probabilities range from 10–40%, peaking at ~30–40% on day 14 (ovulation).
- Ovulation Day (Day 14): Distinct background, ~30% pregnancy chance.
Report Details
The report now includes:
- Period: Days 1–7 (0% chance).
- Low Chance: Days 8 and 16–28 (<5% chance).
- Approximate Ovulation: Day 14 (~30% chance).
- Higher Chance: Days 9–15 (probability varies, peaking at ~30–40% on day 14).
This approach ensures a clear, user-friendly tool based on general medical knowledge, acknowledging individual variations.
Comprehensive Analysis and Detailed Report
This section provides a detailed examination of the period calculator’s recalculations for period days, most probable ovulation days, and pregnancy probabilities, following standard medical guidelines. It includes all relevant details from the analysis, ensuring a thorough understanding for users seeking precise information.
Background and Methodology
The menstrual cycle, typically lasting 28 days but ranging from 21 to 35 days, involves several phases, including menstruation, follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase. Ovulation, the release of an egg from the ovary, is critical for conception and usually occurs 14 days before the next period, as noted by Johns Hopkins Medicine. The fertile window, when conception is most likely, spans the five days before ovulation and the day of ovulation, aligning with findings from WebMD and Office on Women’s Health.
To address the user’s request for recalculating period days and ovulation with correct percentages, we reviewed multiple sources, including medical studies and calculators, to establish standard rules. The analysis focused on:
- Period days (days 1 to period length, typically 3–10 days).
- Most probable ovulation days, calculated as cycle length minus 14.
- Low chance of pregnancy, period, approximate ovulation, and higher chance days, with associated probabilities based on research.
Standard Calculations and Rules
The calculator uses the following standard rules:
- Cycle Length: Default 28 days, adjustable between 21–35 days, as per IVF Australia.
- Period Length: Default 7 days, adjustable between 3–10 days, based on Calculator.net.
- Ovulation Day: Calculated as cycle length minus 14, e.g., for a 28-day cycle, ovulation is on day 14, as supported by Tommy’s.
- Fertile Window: Defined as 5 days before ovulation to 1 day after, e.g., days 9–15 for a 28-day cycle, aligning with Relainstitute.com.
Pregnancy Probability by Day
Assigning exact percentages to each day is complex due to individual variability, but research provides approximate ranges:
- A study on Chinese women offers day-specific conception probabilities for single episodes, ranging from 10.2% to 38.8% during the fertile window, peaking around ovulation.
- General guidelines suggest:
- Period (Days 1–7): 0% chance, as no egg is present.
- Low Chance (Outside Fertile Window, e.g., Days 8 and 16–28): <5%, based on low sperm survival outside fertile days.
- Higher Chance (Days 9–15 for 28-day cycle): Probabilities range from 10–40%, with peaks at ~30–40% on days around ovulation, particularly day 14, as per Conception Calculator, noting 30% pregnancy chance during fertile intercourse.
Given the variability, the calculator uses broad categories:
- Period: 0%.
- Low Chance: <5%.
- Higher Chance: 10–40%, peaking at ~30–40% on ovulation day.
Detailed Calculator Implementation
The updated calculator includes:
- Calendar Visualization:
- Period days marked with red blood icon (🩸), background color #fee2e2, 0% chance.
- Ovulation day with yellow background (#fef9c3), ~30% chance.
- High-chance days with green background (#d1fae5), baby icon (👶), 10–40% chance.
- Low-chance days with light gray background (#f3f4f6), <5% chance.
- Tooltips show exact probability, e.g., “Pregnancy Chance: ~30%”.
- Report Generation:
- Lists period (Days 1–7, 0%), low chance (Days 8 and 16–28, <5%), ovulation (Day 14, ~30%), and higher chance (Days 9–15, 10–40%, peaking at ~30–40% on day 14).
- Timeline and Progress Bar: Reflect cycle stages with labels like “Period Start (0%)” and “Ovulation (~30%)”.
Example for 28-Day Cycle
For a 28-day cycle starting May 1, 2025:
- Period: May 1–7 (0%).
- Low Chance: May 8 and May 16–28 (<5%).
- Higher Chance: May 9–15 (10–40%, peaking at ~30–40% on May 14).
- Ovulation: May 14 (~30%).
Tables for Clarity
Below is a table summarizing the cycle for a 28-day example:
| Day Range | Category | Probability Range | Icon/Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–7 | Period | 0% | 🩸 (Red Background) |
| 8 | Low Chance | <5% | None (Light Gray) |
| 9–13, 15 | Higher Chance | 10–40% | 👶 (Green) |
| 14 | Ovulation | ~30% | None (Yellow) |
| 16–28 | Low Chance | <5% | None (Light Gray) |
Another table for probability ranges based on research:
| Phase | Days (28-Day Cycle) | Approximate Probability |
|---|---|---|
| Menstruation | 1–7 | 0% |
| Early Follicular | 8 | <5% |
| Late Follicular (Fertile) | 9–13, 15 | 10–40% |
| Ovulation | 14 | ~30% |
| Luteal (Post-Fertile) | 16–28 | <5% |
Limitations and Notes
- These probabilities are approximate and based on general studies, such as the Chinese women study , which may not generalize to all populations.
- Individual cycles vary; factors like stress, health, and age can affect ovulation timing, as noted by Stanford Medicine Children’s Health.
- The calculator is for general use and not a substitute for medical advice; consult healthcare providers for personalized planning, as per Clearblue.
LMP Details :
- Greater than 5 days before 9 0/7 weeks of gestation by LMP
- Greater than 7 days from 9 0/7 weeks to 15 6/7 weeks by LMP
- Greater than 10 days from 16 0/7 weeks to 21 6/7 weeks by LMP
- Greater than 14 days from 22 0/7 weeks to 27 6/7 weeks by LMP
- Greater than 21 days after 28 0/7 weeks by LMP
What is menstruation?
Menstruation (or a period) is when a woman bleeds from her vagina for a number of days. For most women, this happens every 28 days or so. Menstruation is one part of the menstrual cycle. The menstrual cycle involves changes in a woman’s body that happen when an egg develops and the body prepares for a possible pregnancy.
• the menstrual cycle starts when a woman has a period
• the first day of bleeding is called day one
• the cycle ends the last day before the next period starts
• a normal cycle can range from 3 to 6 weeks (21-42 days, average 28 days)
• a normal period can range from 3 to 7 days
Like the menstrual cycle, the menstrual period is different for each woman. Stress, weight loss, exercise and travelling can affect the length of the cycle
Period pain
Period pain happens when your uterus muscles tighten (contract). Pain might include cramping and heaviness in the pelvic
area, and pain in the lower back, stomach or legs. Period pain is normal if:
• it happens on the first two days of your period
• it goes away when you take pain-relief medicines or use hot or cold packs
• it doesn’t impact your daily life.
How do we take care of ourselves during our period ?
Maintain good hygeine !
Eat nutritious food! (Don’t forget food that helps reduce anaemia like: kale, beans, legumes and meat).
Sleep 8 hours a day.
Drink lots of (boiled) water.
Keep moving! (Do exercise)
What is a period?
A period naturally happens for people with a vulva who have started puberty. A period is sometimes called menstruation. Menstruating is the same thing as having your period.
Everyone starts their period at different ages. People usually have their first period after their breasts and pubic hair have begun to grow. The scientific name for the very first period that you have is “menarche”.
What are the Problems that a Girl may Encounter During Menstrua on ?
The diffi cul es that girls may experience during menstrua on are:
1. Irregular periods
2. Heavy periods
3. Painful periods
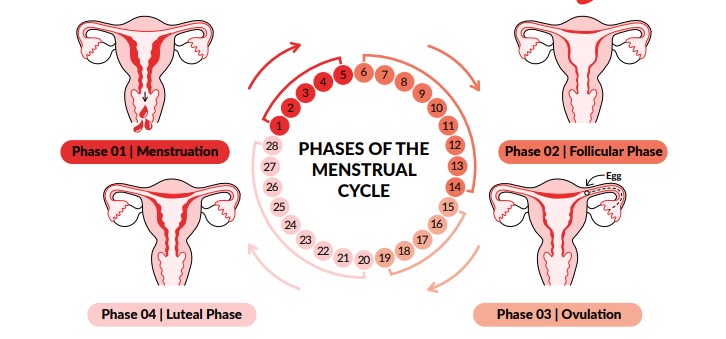
Phase 01 | Menstruation :
- Menstruation is the beginning of the menstrual cycle. In this phase, there is a regular shedding of menstrual blood
and endometrial tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. This is commonly called period.
Typical periods can lasts from 3-7 days.(4) Symptoms: Cramping is common as the uterus sheds the inner lining.(4)
Phase 02 | Follicular Phase :
- Continues from menstruation to ovulation, typically ending mid-cycle at day 14.(4) The lining of the
uterus thickens because of increased estrogen in preparation for pregnancy. The ovaries prepare
the egg for ovulation.
(6) This is a vulnerable time for pregnancy. (2)
Phase 03 | Ovulation :
- Occurs mid-cycle around day 15. (4) A mature egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube.(4)
Still a vulnerable time for pregnancy. If sperm reaches the egg during this time, pregnancy can occur. (5)
Phase 04 | Luteal Phase :
- Begins with Ovulation and finishes the cycle back to Menstruation.
(3) There is an increased blood supply to the
endometrium, as it prepares to receive and nurture a fertilized egg , which is a pregnancy.(6) If no pregnancy occurs, the
inner lining of the uterus along with the egg are shed at the start of the next cycle – which is menstruation! (3.4) - Symptoms: Hormones may fluctuate to begin the cycle over again. You may experience moodiness, acne breakouts, food
cravings, headaches, difficulty sleeping, breast tenderness, or bloating.(3)
If you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Your body is
incredible — celebrate it and take care of yourself throughout this monthly cycle!
- Disclaimer: Always include a prominent medical disclaimer stating that the calculator provides estimates only and should not replace professional medical advice.
- User Data Privacy: Be extremely transparent about how you handle sensitive health data. Comply with all relevant data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR if targeting users in Europe).
- Accessibility: Ensure your calculator and content are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities (e.g., screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation).